Project overview
Public Transport Infrastructure in Central Europe – facilitate transitioning to circular economy
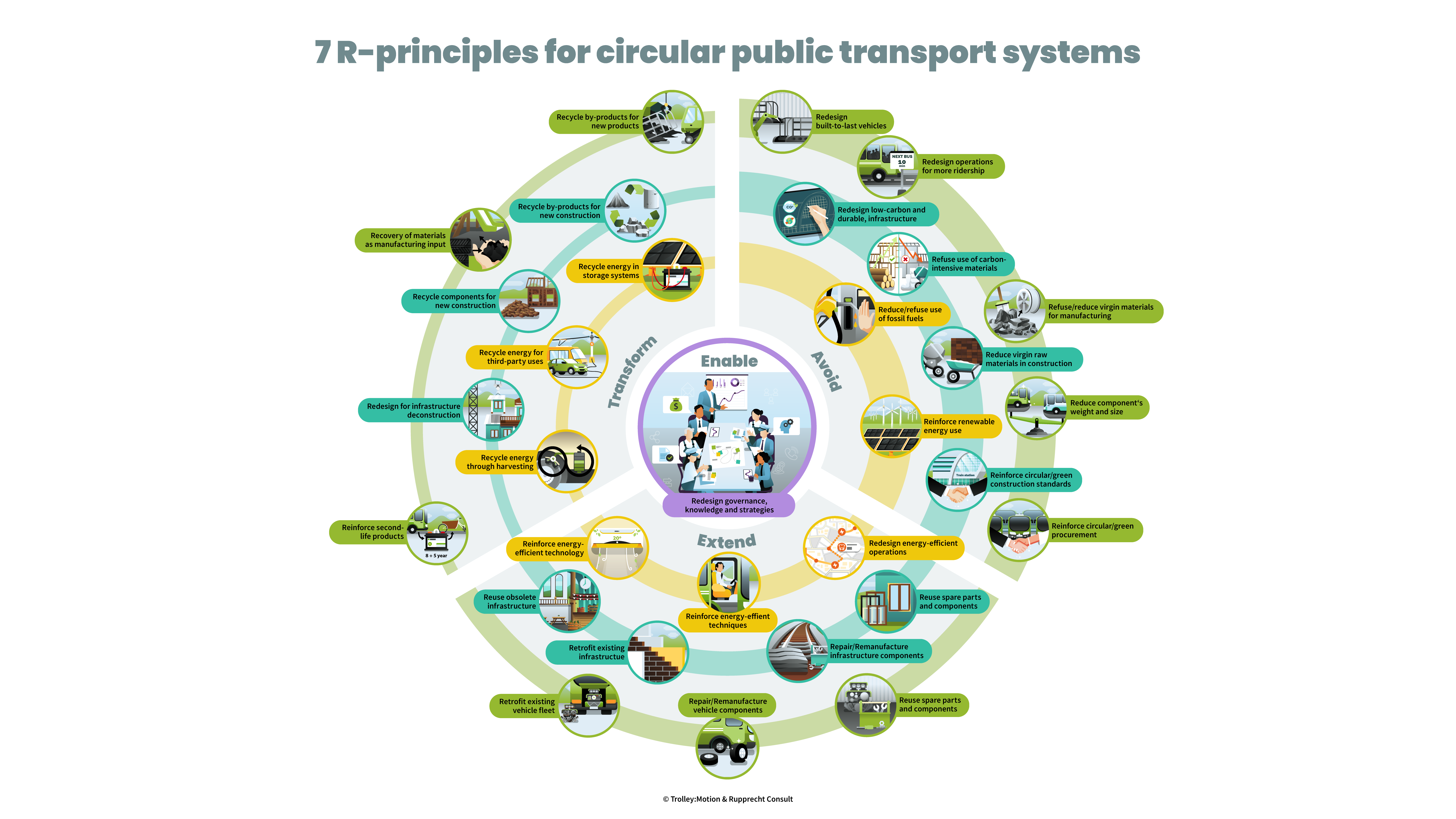
Public transport helps to lower emissions but it is still resource- and waste-intensive in itself. The CE4CE project reduces the ecological footprint of public transport through a higher circularity. The partners identify circularity gaps and develop innovative circular economy models for planners and operators. They provide guidance on how to incorporate circular economy principles into procurement processes for services and infrastructure and design more circular products and business models.
-
2,73m €
-
Project Budget
-
80%
-
of the Budget is funded by ERDF
-
6
-
Countries
-
8
-
Regions
-
11
-
Partners
-
6
-
Pilots
Duration
Start date
End date
Project progress
About the project
Project partnership
Project partners

Lead partner
Leipzig Public Transport Company
Infrastructure
Project partner
Higher Economics School
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Transportation Engineering and Architecture
Roadmap
Context
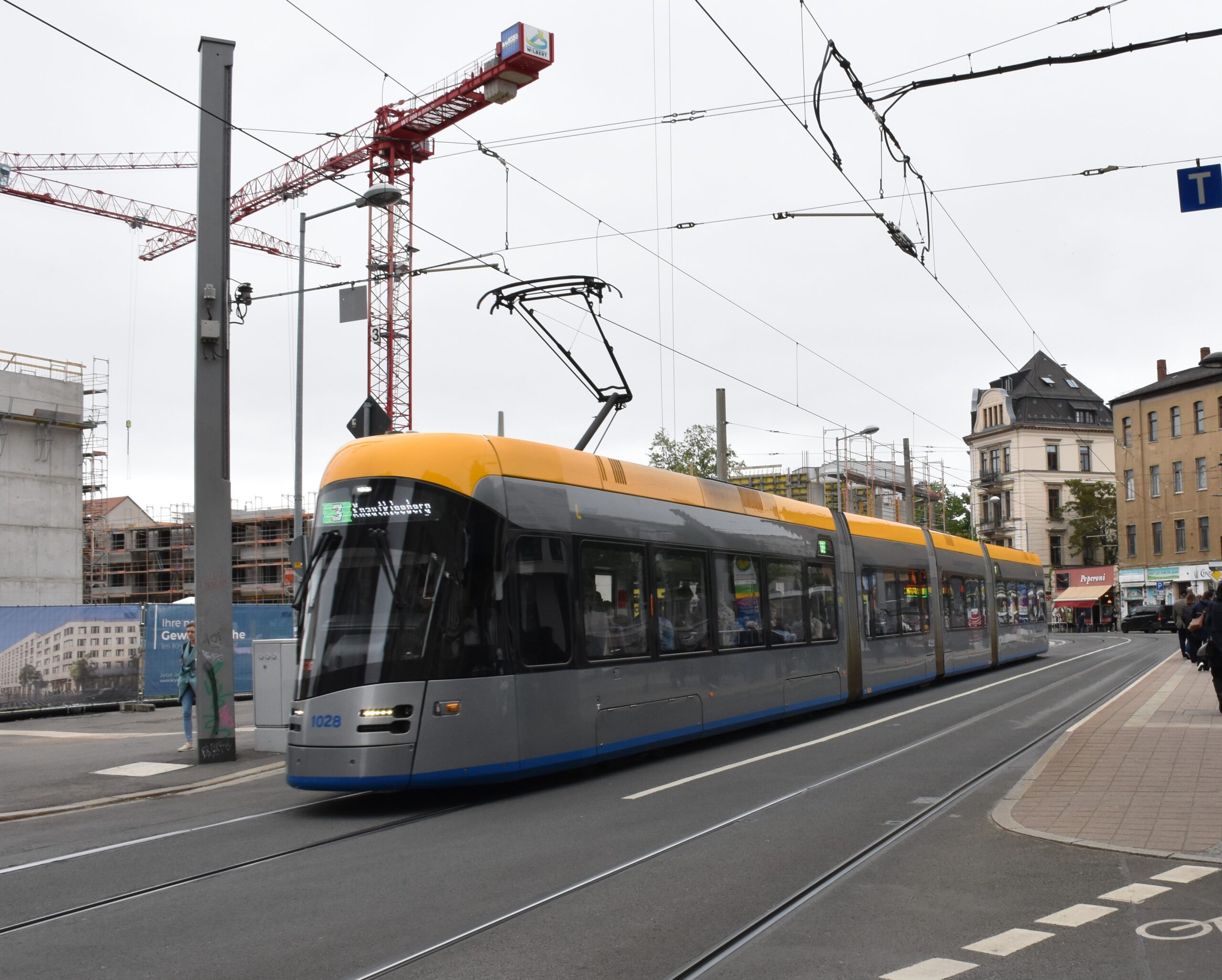

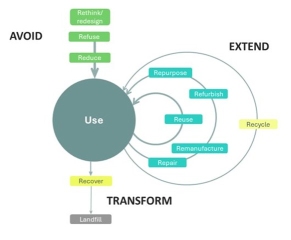
CE4CE addresses challenges related to the need to support circular design and create circular economy related strategies and action plans to reduce environmental degradation and the impact of climate change in the public transport sector. Regarding the basic circular principles “reduce, reuse, use longer, recycle” many countries are still lagging behind European average.
Identified problems
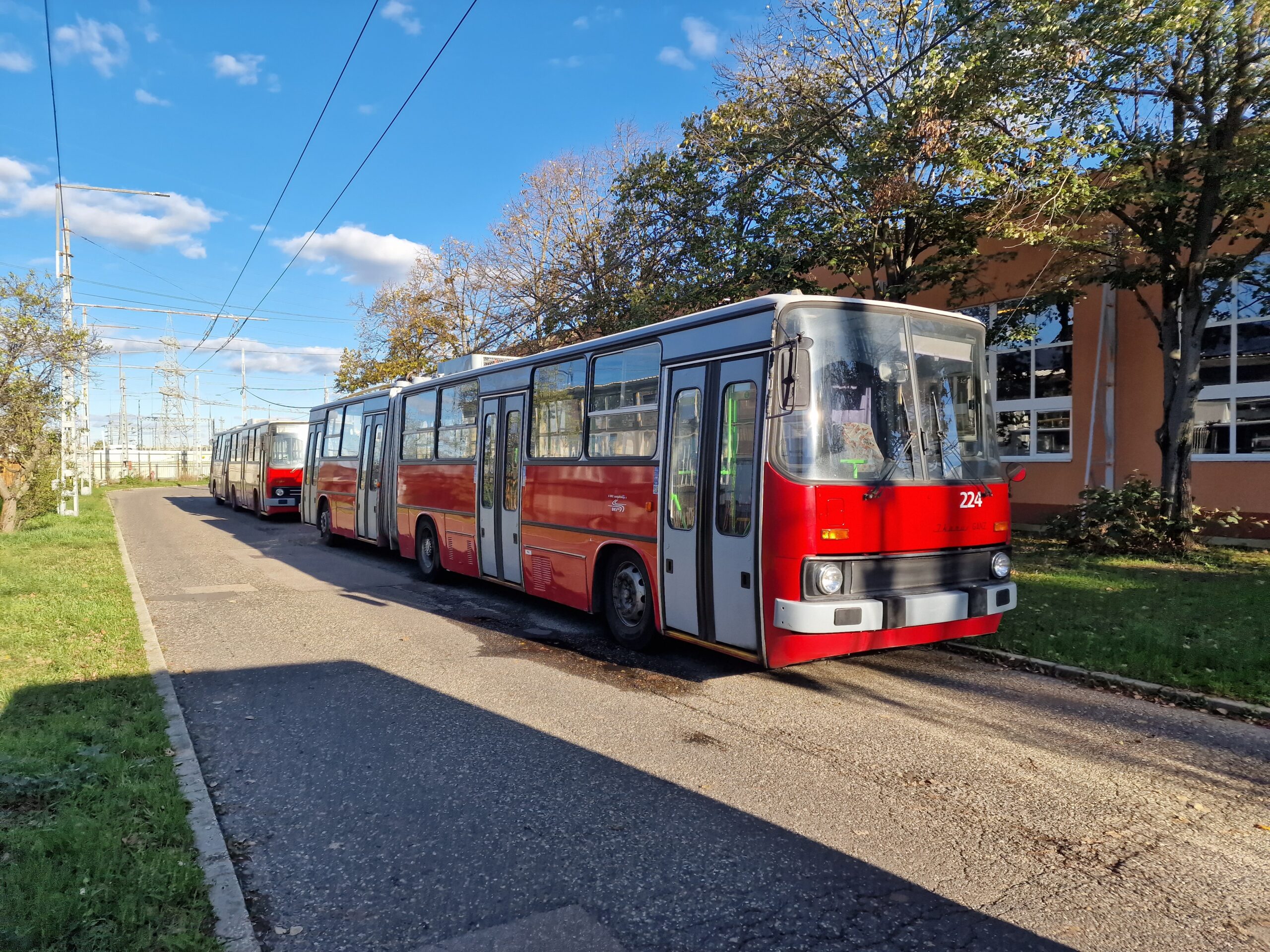

Stakeholders from the public transport sector in Central Europe face the problem of understanding the benefits to applying circular economy principles, identifying circularity gaps in transport infrastructure, energy and rolling stock.
Our challenge
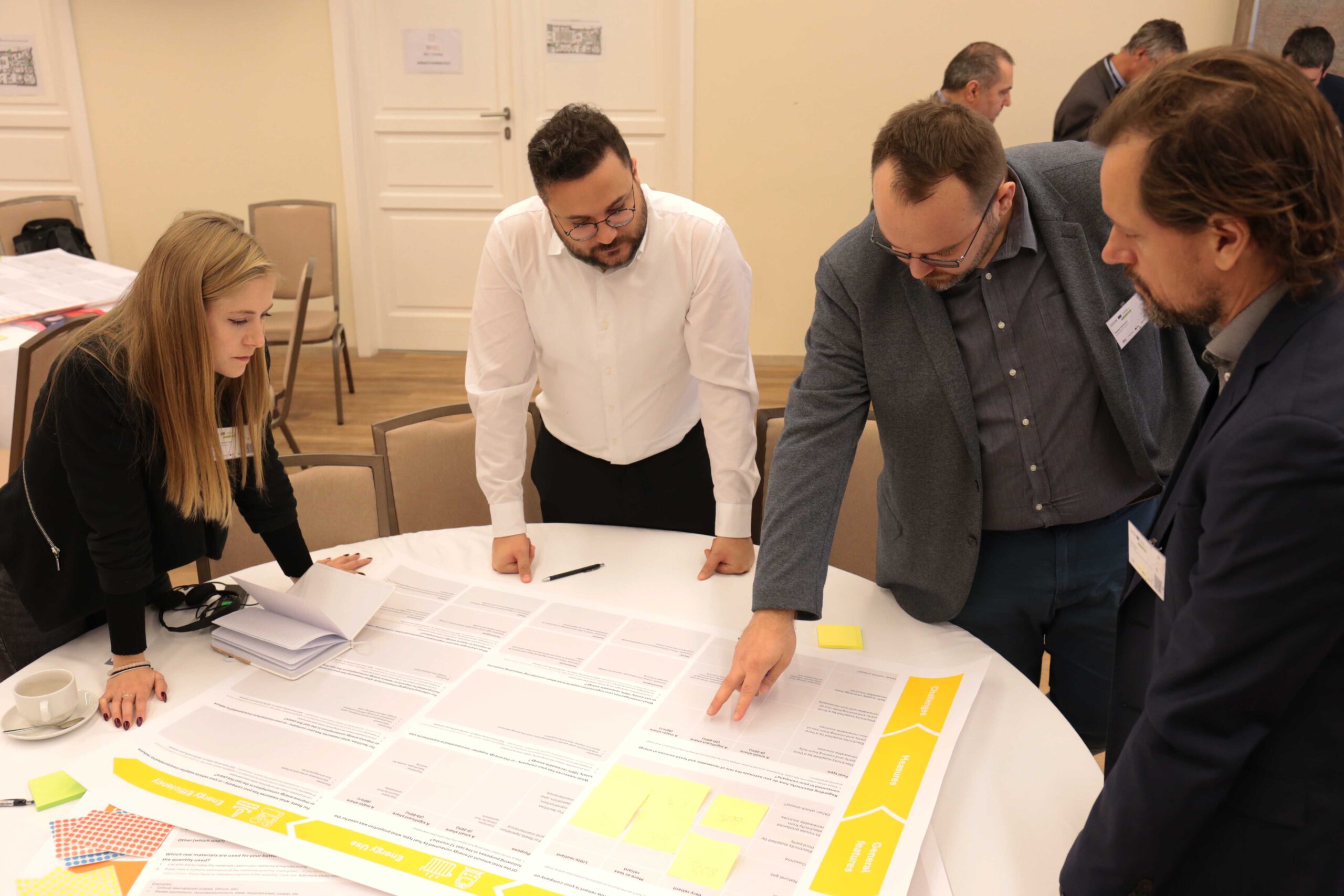

CE4CE embeds circular economy principles in public transport to reduce waste and identify circularity gaps. The goal is to break the unsustainable linear patterns of production and consumption (take-make-use-dispose) by integrating circular principles (reduce, reuse, use longer, recycle) to improve the sustainability of public transport.
Solutions
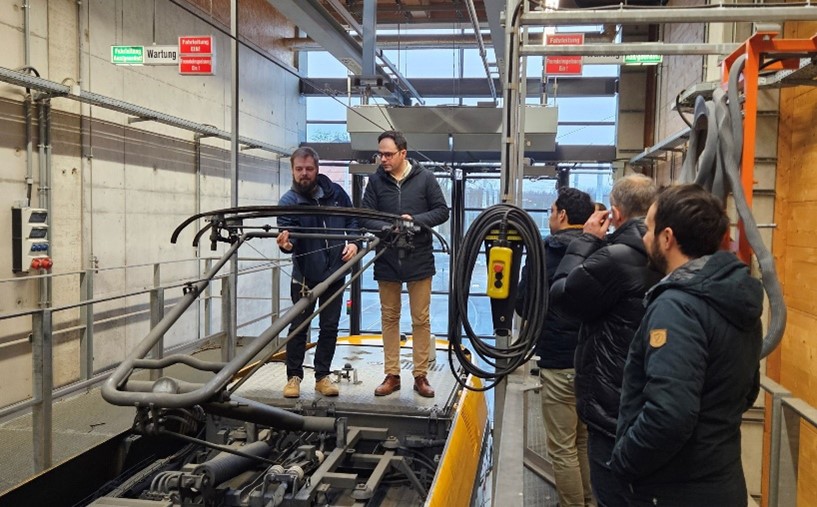

CE4CE aims for a comprehensive circular system thinking approach for the public transport sector, and thus, the project will do a lot of pioneering work and produce numerous first-of-its-kind innovations, such as the Circularity Compass, the Knowledge platform, jointly developed circular strategies and action plans and testing pilots for a circular public transport.
News
Events
Pilot actions
Outputs
Public Transport Circularity Knowledge Platform (output O 1.2)

Strategy to capture and optimize use of waste energy and renewable energy sources along new life cycle value chains (output O 2.1)

Strategy to add and recapture value and optimise delivery of public transport infrastructure along new life cycle value chains (output O 2.2)

Strategy to add & recapture value and optimise delivery of rolling stock / vehicles along new life cycle value chains (output O 2.3)

Action Plan to capture and use waste energy from trains, charge used batteries with renewable energy sources along new life cycle value chains based on municipal circular economy strategy and urban regeneration plan in Maribor (output O 2.4)

Action Plan to optimise delivery of infrastructure through minimal invasive maintenance work in Leipzig (output O 2.5)

Action Plan to optimise delivery of infrastructure by cooperation and sharing between public transport service providers as update of municipal strategy for electromobility in Gdynia (output O 2.6)

Action Plan to add value on the forward supply chain and optimise delivery of vehicles by circular procurement in Bergamo (output O 2.7)

Modules for predictive maintenance of infrastructure and rolling stock (output O 3.2)

Circular business planning tool for electrified public transport fleets and infrastructure (output O 3.4)

Definition of uptake criteria to re-use trolleybus switches (output O 3.6)

Develop transferable business models for re-use of batteries to store renewable energy sources in public transport systems (output O 3.8)

Online second-hand and match-making market for used parts, products and information-sharing to crowdsource circular product-design based on information-sharing (output O 3.10)
Project documents
Newsletter
Project images
CE4CE
The project lead partner is responsible for the content of this project website.